Bootstrap Paradox
The Consequences of the Bootstrap Paradox
Time travel has long been a fascinating concept in science fiction, leading to many intriguing thought experiments and paradoxes. One such paradox that often captures the imagination of readers and viewers is the Bootstrap Paradox.
What is the Bootstrap Paradox?
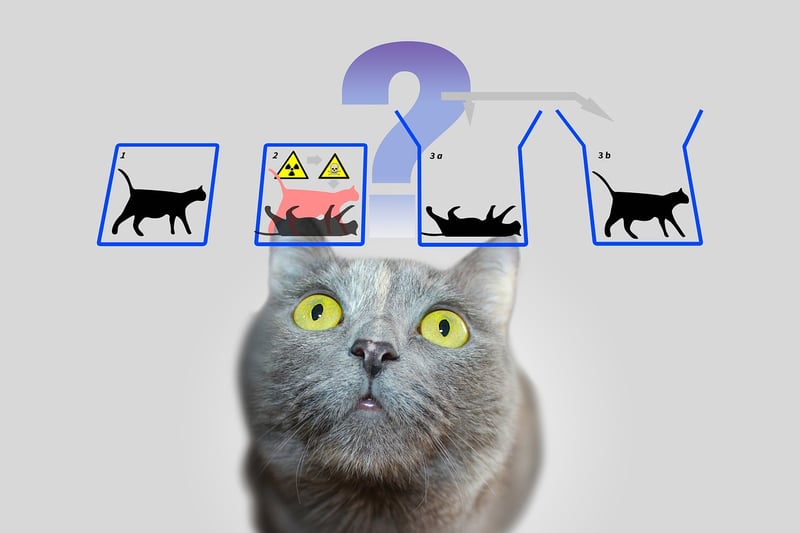
The Bootstrap Paradox, also known as a causal loop, occurs when an object or information is sent back in time and becomes trapped in an infinite loop with no point of origin. In simpler terms, it raises the question of how something could exist without ever being created.
Consequences of the Bootstrap Paradox
One of the most significant consequences of the Bootstrap Paradox is the potential breakdown of cause and effect. In a universe where information or objects can exist without a beginning, the traditional concept of cause leading to an effect is rendered meaningless.
1. Existence without Creation
Objects or information stuck in a Bootstrap Paradox exist without having been created by any known means. This challenges our fundamental understanding of how things come into existence and raises philosophical questions about the nature of reality.
2. Perpetual Loops
Once caught in a Bootstrap Paradox, the object or information perpetually loops through time with no clear origin. This can create a sense of inevitability and determinism, where events are predestined to happen in a never-ending cycle.
3. Paradoxical Causality
The Bootstrap Paradox blurs the line between cause and effect, as the object or information influences its own creation without an external cause. This self-referential loop challenges our understanding of linear time and traditional notions of causality.
Conclusion
The Bootstrap Paradox is a mind-bending concept that challenges our understanding of time, causality, and existence. Exploring the consequences of this paradox can lead to thought-provoking discussions about the nature of reality and the limitations of human comprehension.

For more information on time travel and paradoxes, check out this Wikipedia article.